Rewiring Your Brain: The Profound Impact of Meditation on Neuroplasticity
In the relentless pursuit of optimal mental well-being and peak cognitive performance, few practices rival the transformative power of meditation. Far from being merely a relaxation technique, consistent meditation actively engages the brain’s incredible capacity for change, a phenomenon known as meditation neuroplasticity. This comprehensive guide dives deep into how regular meditative practice can literally facilitate brain rewiring, enhancing mental resilience, sharpening focus, and improving emotional regulation.
💡 Key Takeaways
- Meditation is scientifically proven to induce physical and functional changes in the brain through neuroplasticity.
- Regular practice can increase gray matter in key brain regions linked to attention, emotion regulation, and self-awareness.
- Understanding neuroplasticity empowers individuals to actively ‘rewire’ their brains for improved mental well-being and resilience.
- The profound impact extends beyond stress reduction, offering tangible benefits for cognitive function and emotional intelligence.
“The consistent practice of meditation is a powerful catalyst for neuroplastic change, allowing us to sculpt our own neural pathways towards greater resilience and clarity.”
— Dr. Aris Thorne, Cognitive Neuroscientist & Author
Understanding how meditation interacts with your brain’s intricate structure and dynamic function is key to unlocking its full potential. For a broader perspective on optimizing your cognitive abilities and achieving mastery over your internal landscape, explore our definitive guide on biohacking your mind and achieving mental state control.
In This Article
- → Rewiring Your Brain: The Profound Impact of Meditation on Neuroplasticity
- — 💡 Key Takeaways
- → Understanding Neuroplasticity: The Brain’s Remarkable Capacity for Change
- → The Mechanism of Change: How Meditation Promotes Brain Rewiring
- — ⚙️ Targeting Key Brain Regions and Networks
- → Evidence-Based Transformations: Structural and Functional Brain Changes
- — 📊 Structural Adaptations Observed:
- — ⚡ Functional Adaptations Observed:
- → Practical Applications: Cultivating Neuroplasticity Through Meditation
- — 🧘♀️ Types of Meditation for Brain Rewiring:
- — 🗓️ Tips for Consistent Practice to Maximize Neuroplasticity:
- → Conclusion: A Smarter, More Resilient Brain Through Meditation
Understanding Neuroplasticity: The Brain’s Remarkable Capacity for Change
Neuroplasticity, often referred to as brain plasticity, is the brain’s remarkable ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. It allows neurons to compensate for injury and disease, and to adjust their activities in response to new situations, learning experiences, or changes in the environment. This constant adaptation is fundamental to processes like learning, memory formation, and even recovery from certain types of brain damage.
- ✅ Adaptive Plasticity: This refers to the brain’s ability to strengthen beneficial connections and create new, more efficient `neural pathways` in response to positive experiences or training. It’s how we learn new skills and adapt to new information.
- 🧠 Maladaptive Plasticity: Conversely, the brain can also form unhelpful or detrimental connections, such as those observed in chronic pain pathways or addictive behaviors. Understanding this distinction highlights the importance of intentional practices that foster positive changes.
The concept of `brain rewiring` is central to neuroplasticity, signifying the dynamic reorganization of neural circuits and connections based on repeated experiences and sustained mental stimuli. Meditation provides precisely this kind of sustained mental training.
The Mechanism of Change: How Meditation Promotes Brain Rewiring
Meditation is not merely a passive activity; it’s an active mental training that directly influences neuroplasticity. Through focused attention, repeated concentration, and conscious emotional regulation, it drives significant `structural brain changes` and `functional brain changes`.
⚙️ Targeting Key Brain Regions and Networks
Consistent meditation practice has been shown to impact several critical brain areas and their interconnections:
Meditation’s Impact on Neuroplasticity: Pros and Cons
Pros
- ✔Promotes positive structural and functional brain changes.
- ✔Enhances cognitive functions like attention and memory.
- ✔Reduces stress-related brain atrophy and fosters resilience.
- ✔Supports the development of beneficial habits and emotional regulation.
Cons
- ✖Requires significant time and consistent practice for lasting effects.
- ✖Benefits may not be universally experienced or immediately apparent.
- ✖Potential for initial discomfort or challenging emotional surfacing.
- ✖Not a substitute for professional medical or psychological treatment for severe conditions.
- Prefrontal Cortex (PFC): This region is the brain’s command center, associated with executive functions such as attention, decision-making, planning, and emotional regulation. Meditation strengthens connections here, leading to improved sustained focus, better impulse control, and enhanced cognitive flexibility.
- Hippocampus: A vital component of the limbic system, the hippocampus is crucial for memory consolidation, spatial navigation, and learning. Studies indicate increased grey matter density in this region among long-term meditators, suggesting enhanced learning and memory capabilities.
- Amygdala: Often called the brain’s “fear center,” the amygdala plays a primary role in processing emotions, particularly fear and anxiety. Meditation can lead to decreased amygdala volume and reduced reactivity to stressful stimuli, fostering greater emotional stability and resilience.
- Insula: Involved in interoception (awareness of internal bodily states), empathy, and self-awareness. Enhanced insula activity through meditation can improve an individual’s connection to their physical sensations and their capacity for compassion.
By repeatedly engaging and training these regions, meditation strengthens beneficial `neural pathways` and, importantly, can weaken less desirable ones (e.g., those associated with rumination or anxiety). This process is akin to regular physical exercise for muscles, building stronger, more efficient neurological connections. Some individuals find that supplements like Neurodrine, which are designed to support overall brain health and cognitive function, can potentially complement their meditation practice by fostering an optimal neurological environment for these profound changes to occur.
Evidence-Based Transformations: Structural and Functional Brain Changes
Cutting-edge research utilizing advanced neuroimaging techniques such as fMRI (functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and EEG (Electroencephalography) has provided compelling evidence for the profound impact of meditation on the brain’s architecture and activity. These studies consistently highlight both significant `structural brain changes` and measurable `functional brain changes`.
📊 Structural Adaptations Observed:
- ✅ Increased Grey Matter Density: Research has consistently shown an increase in grey matter density in specific brain regions among meditators, particularly in areas related to attention, emotional regulation, and self-awareness (e.g., the insula, hippocampus, and parts of the prefrontal cortex). This indicates a physical thickening of brain tissue involved in these higher-order functions.
- 🧠 Enhanced White Matter Integrity: White matter forms the crucial communication highways of the brain, facilitating connections between different regions. Improved white matter integrity, observed in long-term meditators, means faster, more efficient communication and information processing along key `neural pathways`.
- ✨ Reduced Amygdala Volume: As mentioned, studies have correlated consistent meditation with a decrease in the size and activity of the amygdala, which directly translates to reduced stress reactivity, anxiety levels, and a greater capacity for emotional resilience.
⚡ Functional Adaptations Observed:
- ✅ Altered Resting-State Networks: Meditation can reconfigure the brain’s default mode network (DMN), a network of brain regions active when the mind is at rest or wandering. Regular practice often leads to less DMN activity, resulting in reduced mind-wandering, less self-referential thought, and greater presence in the moment.
- 🧠 Improved Brainwave Patterns: Regular meditation can lead to a shift in brainwave activity, promoting an increase in beneficial brainwave states, such as alpha and theta waves. These states are associated with deep relaxation, creativity, and profound contemplative insights. To delve deeper into these fascinating electrical rhythms of the brain, explore our guide on understanding brainwave patterns.
- ✨ Enhanced Functional Connectivity: One of the most significant `functional brain changes` is the strengthened functional connections between the prefrontal cortex (the control center) and the amygdala (the emotion center). This enhanced connectivity allows for better top-down emotional regulation, meaning you gain a greater ability to manage your emotional responses rather than being overwhelmed by them.
These demonstrable and measurable changes underscore how meditation isn’t just about feeling better in the moment, but about fundamentally changing the underlying neurological landscape of the brain for long-term benefit. For a deeper dive into the specific neurological shifts and the science behind them, consider exploring our comprehensive article on the neuroscience behind meditation.
Supporting overall brain health with supplements like CogniCare Pro, which aims to enhance cognitive function and mental clarity, can potentially create a more receptive and fertile environment for these neuroplastic changes to occur. By nourishing the brain, individuals may find they can maximize the profound benefits of their meditation practice. For further reading on how mindfulness can effectively rewire your brain, you can consult resources such as this article from Boston University.
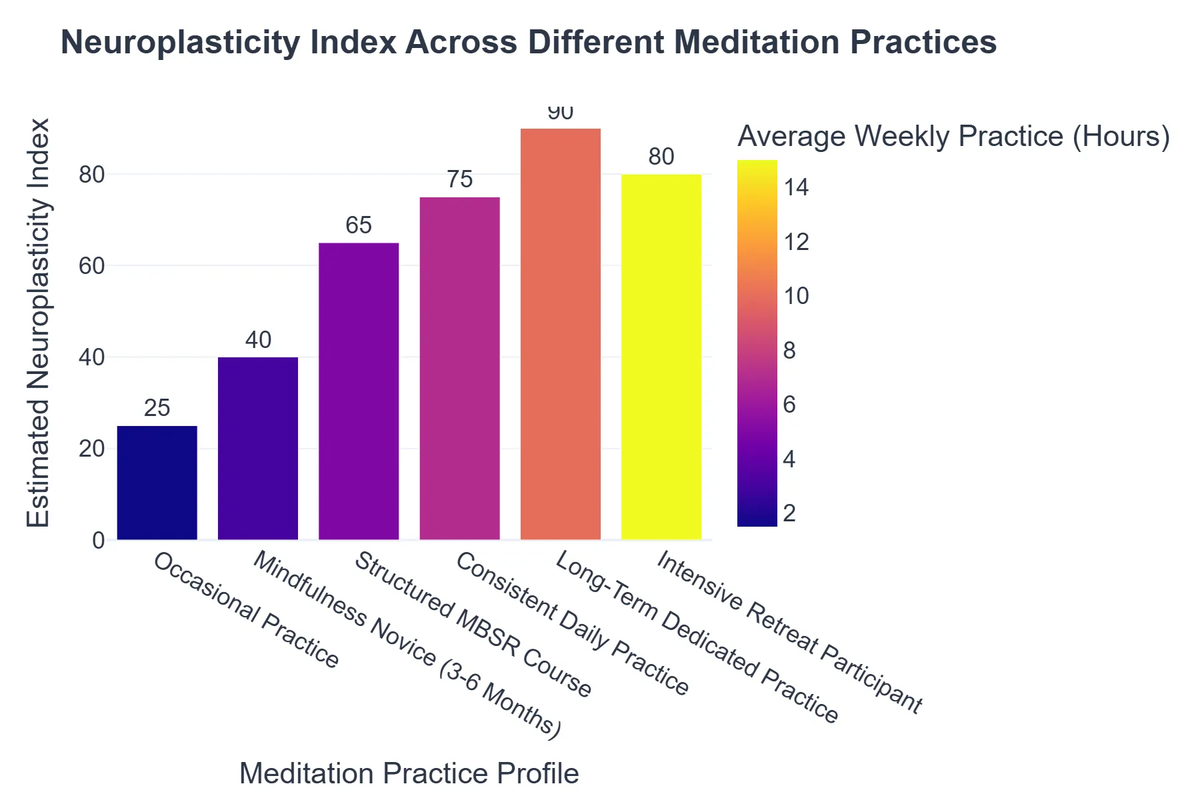
Practical Applications: Cultivating Neuroplasticity Through Meditation
Engaging in a consistent meditation practice is the most direct and effective way to leverage its profound neuroplastic benefits. Even short, regular sessions can yield significant and measurable results over time.
🧘♀️ Types of Meditation for Brain Rewiring:
- Mindfulness Meditation: This widely practiced form involves focusing on the breath, bodily sensations, and present moment awareness without judgment. It is excellent for strengthening attention networks, reducing mind-wandering, and decreasing emotional reactivity by enhancing the PFC’s control over the amygdala.
- Loving-Kindness (Metta) Meditation: This practice cultivates feelings of compassion, kindness, and goodwill towards oneself and others. It specifically promotes positive emotional `neural pathways` and can increase prosocial behaviors and empathy, impacting areas like the insula.
- Transcendental Meditation (TM): Utilizing a specific mantra to achieve deep states of rest and relaxation, TM has been associated with unique brainwave coherence and deep physiological changes that support overall brain health and reduce stress.
🗓️ Tips for Consistent Practice to Maximize Neuroplasticity:
- ✅ Start Small and Be Consistent: Begin with just 5-10 minutes daily. Consistency is far more important than duration, especially in the early stages, as it builds the habit and reinforces new `neural pathways`. Gradually increase your time as you feel comfortable.
- 🧠 Find a Dedicated Quiet Space: Minimize distractions to enhance your focus and reduce external stimuli. A consistent environment can also serve as a positive cue for your brain to enter a meditative state.
- ✨ Utilize Guided Meditations: For beginners and even experienced practitioners, apps like Calm, Headspace, or Insight Timer can provide structure, instruction, and support, making it easier to stick with your practice and learn various techniques.
- 💡 Be Patient and Persistent: Neuroplastic changes take time. The brain needs repeated exposure and consistent effort to reorganize itself. Don’t get discouraged by perceived lack of progress; every session contributes to the cumulative effect.
The remarkable capacity of the human brain to adapt and change throughout life is a testament to its incredible resilience. Learning more about how to support neuroplasticity through various means, including diet, exercise, and mental training, can further enhance your journey. Explore additional insights on supporting your brain’s adaptive capabilities on Bodybio.
Recommended Video
Conclusion: A Smarter, More Resilient Brain Through Meditation
The scientific evidence is overwhelmingly clear: meditation is an extraordinarily powerful and accessible tool for `brain rewiring`. By actively engaging the principles of meditation neuroplasticity, you’re not merely finding moments of calm or stress reduction; you are fundamentally reshaping your brain’s structure and function. From increasing grey matter density in key cognitive areas and improving emotional regulation to strengthening vital `neural pathways` and enhancing functional connectivity, the profound impact of this ancient practice on our modern brains is undeniable.
Embracing meditation as a core component of your mental wellness strategy empowers you to build a more resilient, focused, and adaptable mind, leading to lasting improvements in overall well-being, cognitive performance, and an enhanced capacity to navigate the complexities of life with greater ease and clarity.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does meditation physically change the brain?
Meditation can increase gray matter density in areas like the hippocampus (learning/memory) and prefrontal cortex (decision-making), while decreasing amygdala volume (fear/stress).
What is neuroplasticity in simple terms?
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s remarkable ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections and pathways throughout life, based on new experiences, learning, or injury.
How long does it take to see the effects of meditation on the brain?
Studies suggest that noticeable brain changes can occur in as little as 8 weeks of consistent, regular meditation practice, even for beginners.
Can meditation help with cognitive decline?
While not a cure, regular meditation may help maintain cognitive function and mitigate age-related decline by enhancing brain areas associated with memory, attention, and executive function.
