Mindfulness vs. Vipassana: What’s the Difference and Which is Right for You?
In the burgeoning world of mind-body practices and mental state control, meditation stands out as a powerful tool for enhancing well-being and cognitive function. As more individuals seek to optimize their mental clarity and emotional resilience, two terms frequently surface: mindfulness and Vipassana. While often used interchangeably, understanding the nuances between mindfulness vs. Vipassana is crucial for anyone looking to deepen their practice.
💡 Key Takeaways
- Mindfulness is a broad concept of present-moment awareness, often a foundational component of Vipassana.
- Vipassana is a specific, ancient Buddhist meditation technique focused on gaining insight into the true nature of reality.
- While Mindfulness can be secular, traditional Vipassana often emphasizes its roots in observing impermanence, suffering, and non-self.
- Choosing between them depends on your goals: broad awareness and stress reduction, or deep insight into suffering’s causes.
“Mindfulness is like learning to see clearly; Vipassana is using that clear vision to understand the nature of everything, from the subtle sensations to the grandest truths.”
— Dr. Elena Ramirez, Professor of Contemplative Studies, Serenity Institute
Both approaches offer profound benefits, yet their origins, techniques, and ultimate aims diverge in significant ways. This comprehensive guide will provide a clear meditation comparison, helping you discern the unique characteristics of each and determine which path aligns best with your personal goals. Whether you’re a curious beginner or an experienced practitioner, mastering these distinctions is a vital step in biohacking your mind and achieving true mental mastery.
In This Article
- → Mindfulness vs. Vipassana: What’s the Difference and Which is Right for You?
- — 💡 Key Takeaways
- → 🧘 What is Mindfulness?
- — ⚙️ Common Mindfulness Practices:
- — ✨ Benefits of Mindfulness Meditation:
- → 🧘 What is Vipassana Meditation?
- — ⚙️ Core Principles of Vipassana Meditation:
- — ✨ Benefits of Vipassana Meditation:
- → 📊 Key Differences: Mindfulness vs. Vipassana
- — Origins & Context:
- — Goals & Aims:
- — Technique & Depth:
- — Intensity & Duration:
- → 🤔 Which is Right for You?
- — Choose Mindfulness If:
- — Choose Vipassana If:
- → Conclusion: Finding Your Path to Mental State Control
🧘 What is Mindfulness?
Mindfulness, in its simplest form, is the practice of being present. It involves paying attention to the present moment, without judgment, to your thoughts, feelings, bodily sensations, and the surrounding environment. While its roots are deeply embedded in Buddhist traditions, mindfulness has been largely secularized and integrated into various therapeutic and self-improvement programs, such as Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR).
The core of mindfulness lies in cultivating awareness. It’s about observing your internal and external experiences as they unfold, rather than getting caught up in them or reacting impulsively. This practice helps to create a mental space, allowing you to respond thoughtfully instead of reactively.
Mindfulness vs. Vipassana: A Comparative Review
Pros
- ✔Mindfulness is highly accessible and adaptable for daily stress reduction and general well-being.
- ✔Mindfulness is often secular, making it broadly appealing without specific spiritual commitments.
- ✔Vipassana offers a structured path to deep insight into the nature of reality and suffering’s root causes.
- ✔Vipassana can lead to profound personal transformation through its rigorous and focused practice.
Cons
- ✖Mindfulness practice may lack the depth of traditional insight if approached superficially.
- ✖The commercialization of mindfulness can sometimes dilute its original transformative purpose.
- ✖Vipassana requires significant time commitment, often involving intensive, silent retreats.
- ✖Vipassana can be psychologically challenging, potentially bringing up difficult emotions without immediate support.
⚙️ Common Mindfulness Practices:
- ✅ Breath Awareness: Focusing attention on the sensation of the breath as it enters and leaves the body. This serves as an anchor to the present moment.
- ✅ Body Scan: Systematically bringing attention to different parts of the body, noticing any sensations without judgment.
- ✅ Mindful Eating: Paying full attention to the experience of eating – the tastes, textures, smells, and even the sounds of chewing.
- ✅ Walking Meditation: Becoming aware of the physical sensations of walking – the lifting and placing of feet, the movement of the body.
✨ Benefits of Mindfulness Meditation:
- 🚀 Reduces stress and anxiety.
- 🚀 Improves emotional regulation.
- 🚀 Enhances focus and attention.
- 🚀 Increases self-awareness and compassion.
- 🚀 Fosters a sense of calm and well-being.
Many beginners find their entry point into meditation through guided meditation, which often centers on mindfulness techniques, making it highly accessible.
🧘 What is Vipassana Meditation?
Vipassana, meaning “to see things as they really are,” is one of India’s most ancient meditation techniques, rediscovered by Gautama Buddha more than 2,500 years ago. It is a rigorous form of “insight meditation” that aims for nothing less than the total eradication of mental impurities and the attainment of liberation and full enlightenment.
Unlike secular mindfulness, Vipassana is taught in a highly structured and traditional manner, often in intensive, silent retreats lasting 10 days or more. The primary technique involves observing the sensations of the body with extreme precision and equanimity, from the grossest to the most subtle, and understanding their impermanent, unsatisfactory, and non-self nature. This profound self-observation leads to deep insights into the workings of the mind and the nature of reality.
⚙️ Core Principles of Vipassana Meditation:
- 🎯 Anapana-sati: The initial stage, focusing on the natural, unmanipulated breath to calm the mind and develop concentration (Samatha). This prepares the mind for deeper insight.
- 🎯 Systematic Body Scan: Moving attention systematically through the body, observing all physical sensations (e.g., tingling, pressure, warmth, coolness) without reacting to them, understanding their impermanence.
- 🎯 Equanimity: Maintaining a balanced and non-reactive mind towards all sensations, whether pleasant, unpleasant, or neutral. This is key to breaking old patterns of craving and aversion.
✨ Benefits of Vipassana Meditation:
- 🧠 Leads to profound self-knowledge and insight into the nature of existence.
- 🧠 Eradicates deep-rooted mental defilements.
- 🧠 Cultivates deep peace and inner harmony.
- 🧠 Develops strong mental discipline and concentration.
- 🧠 Aims for liberation from suffering.
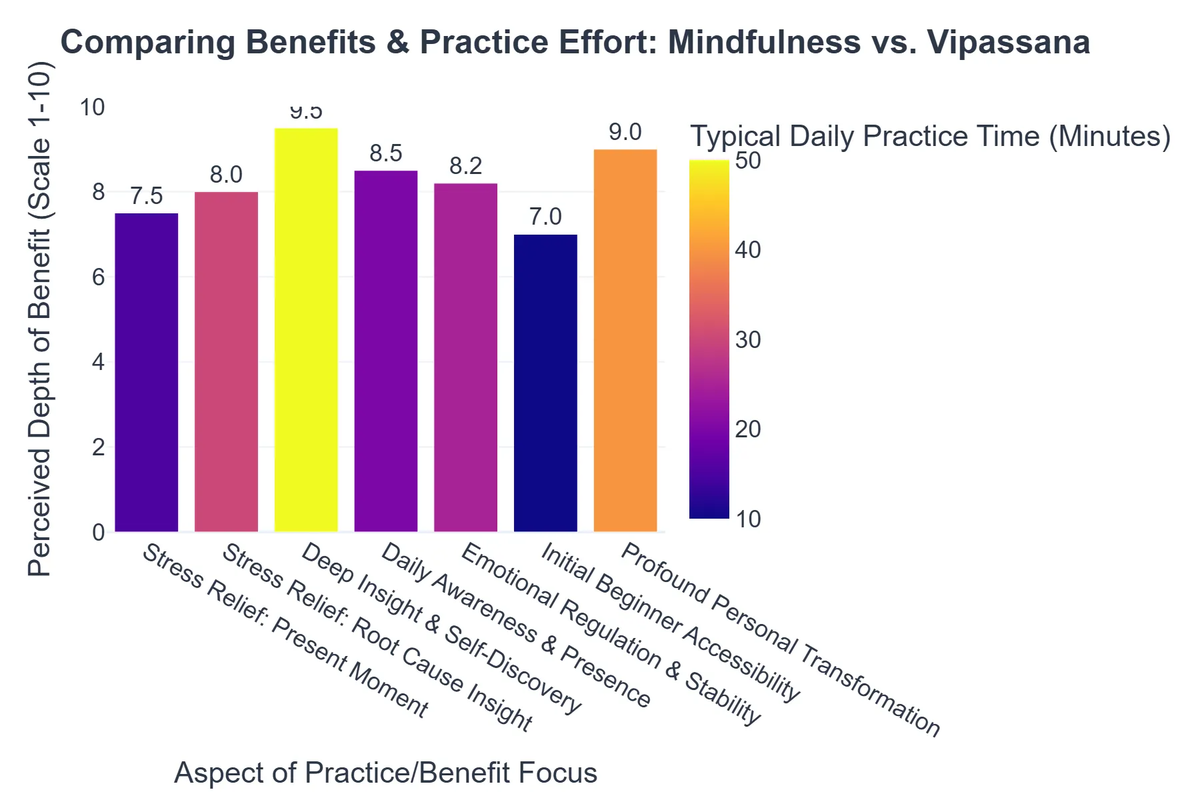
📊 Key Differences: Mindfulness vs. Vipassana
While modern mindfulness can be seen as a component or a simplified offshoot of Vipassana, there are distinct differences that set them apart:
Origins & Context:
- ✅ Mindfulness: Originated in Buddhist traditions but widely secularized and adapted for Western clinical and self-help contexts. Often taught as a standalone practice for stress reduction and well-being.
- ✅ Vipassana: A specific, ancient Buddhist meditation technique. Taught in its traditional form, often within a structured retreat setting, with a clear path towards spiritual purification and enlightenment.
Goals & Aims:
- ✅ Mindfulness: Primarily focuses on stress reduction, improved emotional regulation, enhanced focus, and general well-being in daily life. It aims to improve your experience of the present.
- ✅ Vipassana: Its ultimate goal is to purify the mind, eradicate mental defilements (such as craving, aversion, and ignorance), and achieve full liberation (Nibbana/Nirvana) through direct experience of the impermanent, unsatisfactory, and non-self nature of phenomena.
Technique & Depth:
- ✅ Mindfulness: Often involves focusing on broader aspects of present-moment awareness, such as breath, body sensations, thoughts, and sounds. While depth is possible, the emphasis is often on immediate application and relief.
- ✅ Vipassana: Begins with cultivating strong concentration through breath awareness (Anapana) and then progresses to an intense, systematic, and equanimous observation of subtle, ever-changing physical sensations throughout the body. This meticulous observation is the vehicle for gaining deep insight. As this resource explains, the core difference lies in the “object of observation and purpose” (Buddhism Stack Exchange).
Intensity & Duration:
- ✅ Mindfulness: Can be practiced for short durations (e.g., 5-20 minutes daily) and integrated into daily activities. It’s flexible and adaptable to various lifestyles.
- ✅ Vipassana: Typically requires intensive, silent retreats, often 10 days in length, with 10+ hours of meditation per day. It demands significant commitment and discipline.
🤔 Which is Right for You?
The choice between mindfulness and Vipassana largely depends on your goals, readiness, and the level of commitment you are prepared to undertake. Both practices can significantly impact your mental landscape and enhance practical meditation techniques for brainwave entrainment.
Choose Mindfulness If:
- ✅ You’re a beginner: It offers an accessible entry point into meditation without requiring a major lifestyle overhaul.
- ✅ Your primary goal is stress reduction: You want to manage anxiety, improve focus, and enhance general well-being in daily life.
- ✅ You prefer flexibility: You want to integrate short practices into your daily routine without attending lengthy retreats.
- ✅ You’re looking for secular benefits: You’re not necessarily seeking spiritual enlightenment but practical tools for mental health.
Choose Vipassana If:
- ✅ You seek deep insight and self-purification: You are ready to explore the deepest layers of your mind and confront root causes of suffering.
- ✅ You are prepared for intensity: You are willing to commit to a rigorous, silent retreat setting for an extended period.
- ✅ You are interested in the traditional Buddhist path: You are open to a practice with clear ethical guidelines and a focus on liberation.
- ✅ You have some prior meditation experience: While not strictly necessary, a basic understanding of meditation can be helpful before diving into the intensity of Vipassana.
It’s also worth noting that many who practice Vipassana consider mindfulness (especially Anapana) to be a foundational component. You can certainly begin with mindfulness to build a strong base of concentration and awareness, and then explore Vipassana if you feel called to a deeper, more rigorous path.
Recommended Video
Conclusion: Finding Your Path to Mental State Control
Both mindfulness and Vipassana offer unique and powerful pathways to greater self-awareness and control over your mental state. While mindfulness provides a highly adaptable and secular tool for navigating daily life with greater presence and less stress, Vipassana offers a profound, traditional journey towards deep insight and ultimate liberation from suffering.
Neither is “better” than the other; they simply serve different purposes and cater to varying levels of commitment and spiritual inclination. The key is to understand your own needs and intentions, and then choose the practice that resonates most deeply with your personal journey of mental mastery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Vipassana a type of Mindfulness?
While often intertwined, Vipassana is a specific meditation technique that utilizes mindfulness as a tool to gain insight into the true nature of reality. Mindfulness, in a broader sense, is simply present moment awareness.
Can I practice Mindfulness without practicing Vipassana?
Yes, absolutely. Mindfulness can be practiced independently through various exercises like mindful breathing, walking, or eating, without adhering to the structured Vipassana technique.
Which practice is better for stress reduction?
Both practices can significantly reduce stress. Mindfulness helps by anchoring you in the present, reducing rumination. Vipassana addresses stress by helping you understand its root causes through direct observation of sensations and thoughts.
Do I need to be Buddhist to practice Vipassana?
No, while Vipassana has Buddhist origins, it is widely taught and practiced in secular contexts worldwide, focusing on its practical benefits for insight and liberation from suffering, independent of religious dogma.
