Understanding Brainwaves: A Beginner’s Guide to Alpha, Theta, Delta, and Gamma
In the intricate landscape of the human mind, unseen electrical signals are constantly at work, orchestrating every thought, emotion, and action. These rhythmic electrical impulses, generated by the synchronous activity of millions of neurons, are known as brainwaves. Far from being a static phenomenon, our brainwaves are dynamic, constantly shifting based on our level of consciousness, mental state, and even our physical activity. Understanding these fundamental rhythms offers a profound insight into how our minds work and, more importantly, how we can consciously influence our mental states for improved well-being and performance.
💡 Key Takeaways
- Brainwaves are electrical impulses generated by the brain, reflecting different states of consciousness and mental activity.
- Each brainwave frequency (Delta, Theta, Alpha, Beta, Gamma) is associated with distinct mental states, from deep sleep to high-level cognition.
- Understanding your brainwave patterns can provide insights into your cognitive and emotional well-being.
- Techniques like meditation, mindfulness, and proper sleep hygiene can influence and optimize your brainwave states.
“Our brainwaves are like an orchestra, constantly harmonizing to create our reality. Learning to attune to their rhythm is key to mental mastery.”
— Dr. Evelyn Reed, Cognitive Neuroscientist, Serenity Institute
This guide will demystify the fascinating world of brainwave types, exploring the unique characteristics, associated mental states, and practical implications of the five primary frequency bands: Delta, Theta, Alpha, Beta, and Gamma. Whether you’re a curious beginner or looking to deepen your understanding of mental state control, grasping these concepts is a crucial first step in your journey toward biohacking your mind.
In This Article
- → Understanding Brainwaves: A Beginner’s Guide to Alpha, Theta, Delta, and Gamma
- — 💡 Key Takeaways
- → What Are Brainwaves? The Electrical Language of Your Brain
- — ⚙️ The Basics of Brain Activity
- — 🔬 How Brainwaves Are Measured: An Introduction to EEG
- → The Five Primary Brainwave Frequencies
- — 📊 From Slow to Fast: A Spectrum of Consciousness
- → 🌊 Delta Waves: The Deepest State of Rest
- — Characteristics & Associated States:
- → 💭 Theta Waves: The Gateway to Creativity and Memory
- — Characteristics & Associated States:
- → 🧘 Alpha Waves: The Bridge to Calm and Focus
- — Characteristics & Associated States:
- → 🧠 Beta Waves: The Active and Alert Mind
- — Characteristics & Associated States:
- → ✨ Gamma Waves: The Peak of Cognitive Function
- — Characteristics & Associated States:
- → The Dynamic Interplay of Brainwave States
- — 🎵 Brainwave Entrainment and How It Works
- — 📈 Optimizing Your Brainwave Profile
- → 🚀 How to Influence Your Brainwaves for Optimal Performance
- — 🧘 Meditation and Mindfulness: Directing Your Brain’s Orchestra
- — 🧠 Neurofeedback: Training Your Brain
- — 🎧 Sound and Light Therapy (Binaural Beats)
- — 🍎 Lifestyle Factors: Supporting Your Brain’s Health
- → The Future of Brainwave Understanding and Biohacking
- — 💻 Advancements in Brainwave Technology
- — 🎯 Personalized Brainwave Optimization
- → Conclusion: Harnessing Your Inner Rhythms
What Are Brainwaves? The Electrical Language of Your Brain
At its core, your brain is an electrochemical organ, and its primary mode of communication is electrical. Brainwaves are simply the patterns of electrical activity produced by your brain’s neurons communicating with each other. This activity can be measured using specialized equipment, providing a window into the inner workings of your mind. Think of them as the “language” your brain uses to operate, with different frequencies correlating to different types of information processing and states of consciousness.
⚙️ The Basics of Brain Activity
- ✅ Frequency (Hz): Measured in Hertz (Hz), this refers to the number of cycles per second. Higher frequencies indicate faster brain activity, while lower frequencies suggest slower activity.
- ✅ Amplitude (μV): Measured in microvolts (μV), this refers to the “power” or intensity of the electrical activity. High-amplitude waves indicate more neurons firing in synchronicity.
- ✅ Location: Brainwaves can originate and be more prominent in specific areas of the brain, reflecting localized brain activity related to certain functions.
The interplay of these factors creates the complex symphony of brainwave activity that defines our every moment. For a deeper dive into the mechanics, consider how brainwave frequencies are explained in detail by leading neuroscience resources.
🔬 How Brainwaves Are Measured: An Introduction to EEG
The primary non-invasive method for measuring brainwaves is Electroencephalography (EEG). An EEG involves placing electrodes on the scalp, which detect the tiny electrical voltages produced by the brain’s neurons. These signals are then amplified and recorded, allowing scientists and practitioners to observe and analyze the various brainwave patterns. This technology provides invaluable insights into brain function, aiding in everything from diagnosing neurological conditions to exploring states of consciousness during meditation. To learn more about this foundational technology, refer to comprehensive guides on EEG (Electroencephalography).
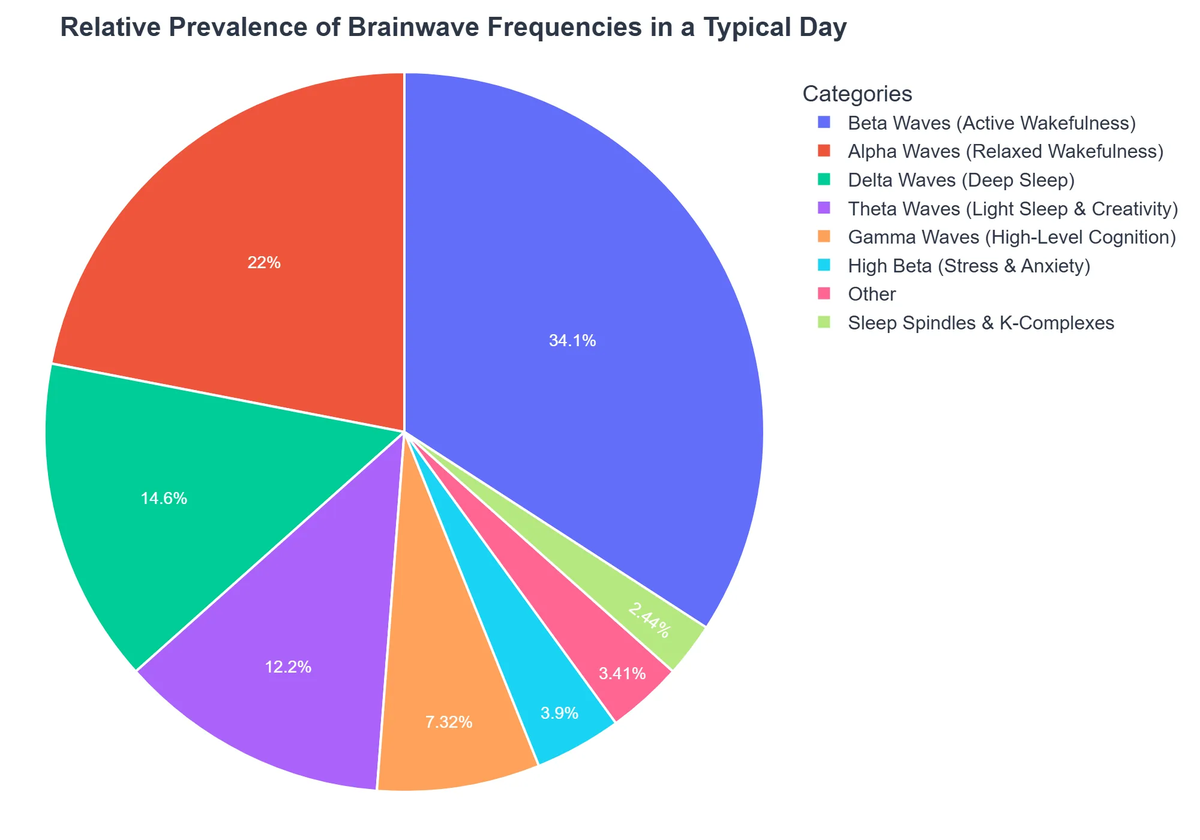
The Five Primary Brainwave Frequencies
While brainwave activity is a continuous spectrum, scientists have categorized them into five primary bands based on their frequency range. Each band is associated with distinct mental states and cognitive functions.
📊 From Slow to Fast: A Spectrum of Consciousness
Understanding the spectrum from slowest to fastest brainwave frequencies helps illustrate the relationship between brain activity and our conscious experience:
- Delta Waves: Deep sleep, unconsciousness.
- Theta Waves: Deep relaxation, meditation, REM sleep, creativity.
- Alpha Waves: Relaxed alertness, light meditation, calm.
- Beta Waves: Active thinking, alertness, concentration, problem-solving.
- Gamma Waves: Peak concentration, high-level processing, insight, heightened perception.
The goal is often not to eliminate any one type of brainwave, but rather to cultivate the ability to shift between these states flexibly and appropriately for the demands of the moment.
🌊 Delta Waves: The Deepest State of Rest
Frequency Range: 0.5 Hz to 4 Hz
Delta waves are the slowest and highest in amplitude of all brainwaves, predominantly associated with the deepest stages of sleep (non-REM sleep). They are crucial for physical regeneration and the restoration of bodily systems.
Characteristics & Associated States:
- ✅ Deep Sleep: When delta activity is dominant, you are in a state of profound unconsciousness, vital for physical healing and immune system regulation.
- ✅ Restorative Processes: Growth hormone release, cellular repair, and physiological recovery largely occur during delta-rich sleep.
- ✅ Unconsciousness: While generally associated with sleep, delta waves can also be present in very deep meditative states or states of deep relaxation, though less commonly and usually accompanied by other frequencies.
Insufficient delta wave activity can lead to feelings of fatigue, poor physical recovery, and a compromised immune system. Cultivating healthy sleep patterns is paramount for optimizing delta wave production.
💭 Theta Waves: The Gateway to Creativity and Memory
Frequency Range: 4 Hz to 8 Hz
Theta waves emerge when you are deeply relaxed, often just before falling asleep, during REM sleep, or in states of deep meditation. They are known as the “subconscious” waves, acting as a gateway to our memories, intuition, and creative insights.
Characteristics & Associated States:
- ✅ Deep Meditation & Mindfulness: Many meditative practices aim to increase theta wave activity, facilitating profound states of inner peace and introspection. This deep mental state control is a core aspect of biohacking your mind.
- ✅ REM Sleep: Associated with dreaming, theta waves play a significant role in memory consolidation and emotional processing.
- ✅ Creativity & Intuition: Artists, musicians, and innovators often experience flashes of insight or “aha!” moments when their brains are producing more theta waves. It’s a state where new connections are easily formed.
- ✅ Learning & Memory: Theta waves are crucial for memory formation and recall, particularly for spatial navigation and episodic memory.
Accessing the theta state can unlock powerful potential for self-discovery, problem-solving, and enhanced learning. Techniques like visualization and guided imagery are often most effective when the brain is in a theta state.
🧘 Alpha Waves: The Bridge to Calm and Focus
Frequency Range: 8 Hz to 12 Hz
Alpha waves are often described as the “bridge” between the conscious and subconscious mind. They are most prominent when you are in a state of relaxed alertness, such as resting with your eyes closed, during light meditation, or when you are in a “flow state.”
Characteristics & Associated States:
- ✅ Relaxed Awareness: Alpha waves indicate a state of calm readiness, where the mind is peaceful but attentive. It’s the ideal state for learning new information without stress.
- ✅ Stress Reduction: Increasing alpha waves can significantly reduce anxiety and promote a sense of well-being. This is a key benefit derived from many relaxation techniques.
- ✅ Light Meditation: Many forms of meditation aim to induce an alpha state, fostering inner calm and reducing mental chatter. Understanding these brainwave shifts is fundamental to the neuroscience behind meditation.
- ✅ Creative Visualization: Alpha is an excellent state for visualization and mental rehearsal, enhancing performance in sports, arts, and professional life.
Cultivating alpha waves is highly beneficial for managing daily stress, improving cognitive flexibility, and preparing the mind for deeper meditative states or focused work. Activities like yoga, gentle walks in nature, and deep breathing exercises are excellent for promoting alpha wave production.
🧠 Beta Waves: The Active and Alert Mind
Frequency Range: 13 Hz to 30 Hz
Beta waves are the dominant brainwave state during our waking hours, particularly when we are actively engaged in cognitive tasks, problem-solving, decision-making, or highly focused activities. They are associated with alertness and outward attention.
Characteristics & Associated States:
- ✅ Active Thinking: When you’re analyzing, reasoning, or solving problems, your brain is typically producing high levels of beta waves.
- ✅ Concentration & Focus: Necessary for daily tasks, work, and any activity requiring sustained attention.
- ✅ Alertness: Beta waves keep us awake, aware of our surroundings, and ready to react.
- ✅ Anxiety & Stress: While essential, an excess of high-frequency beta waves, especially in the higher range (high beta or “high beta anxiety”), can lead to feelings of stress, anxiety, restlessness, and rumination.
Optimizing beta wave activity means finding the right balance: enough to be productive and alert, but not so much that it leads to burnout or overwhelm. Practicing short breaks, mindfulness, and ensuring sufficient alpha/theta time can help balance beta activity.
✨ Gamma Waves: The Peak of Cognitive Function
Frequency Range: 30 Hz to 100+ Hz
Gamma waves are the fastest of all brainwaves, and their role has gained increasing attention in recent neuroscience research. They are associated with moments of peak performance, high-level information processing, and states of profound insight and consciousness.
Characteristics & Associated States:
- ✅ Cognitive Processing: Gamma waves are thought to be crucial for binding information from various brain regions into a coherent whole, facilitating rapid learning and complex problem-solving.
- ✅ Peak Concentration & Focus: When you are “in the zone” or experiencing a moment of intense focus and heightened perception, gamma waves are often prominent.
- ✅ Insight & “Aha!” Moments: Sudden realizations, flashes of intuition, and creative breakthroughs are often accompanied by bursts of gamma activity.
- ✅ Consciousness & Awareness: Some theories suggest gamma waves play a role in our conscious experience and the integration of sensory information.
- ✅ Neuroplasticity: Emerging research indicates that inducing gamma waves, especially through certain meditative practices, may be linked to increased brain plasticity, helping in rewiring your brain.
While often elusive and harder to measure consistently due to their low amplitude, the cultivation of gamma waves is seen as a frontier in optimizing human cognitive potential. Deep meditation, particularly compassion-based practices, has been linked to increased gamma wave activity in experienced practitioners.
The Dynamic Interplay of Brainwave States
It’s crucial to understand that your brain doesn’t operate in just one brainwave state at a time. Instead, all five types are present simultaneously, though usually one or two frequencies will be dominant depending on your current activity and state of consciousness. For example, while you’re reading this, your beta waves are likely dominant, but there’s still underlying alpha, theta, and delta activity supporting other brain functions.
🎵 Brainwave Entrainment and How It Works
Brainwave entrainment is a method used to guide brainwave frequencies towards a desired state. It leverages the brain’s “frequency following response,” where the brain’s electrical activity will naturally synchronize with external rhythmic stimuli. This is often achieved through:
- ✅ Binaural Beats: Two slightly different frequencies are played into each ear, creating a perceived third “beat” frequency within the brain that encourages brainwave synchronization.
- ✅ Monaural Beats: Similar to binaural beats, but the frequencies are mixed before they reach the ears, producing a direct beat perceived by the brain.
- ✅ Isochronic Tones: Regular, evenly spaced pulses of a single tone, which are very effective at entraining brainwaves due to their sharp, distinct on-off nature.
These techniques are widely used to promote relaxation, enhance focus, improve sleep, or stimulate creativity by nudging the brain into alpha, theta, or even delta states.
Understanding Brainwaves: Beginner’s Guide Pros and Cons
Pros
- ✔Increases self-awareness of mental states and cognitive function.
- ✔Provides a foundational understanding for mind-body practices.
- ✔Demystifies complex neurological concepts for a general audience.
- ✔Can spark interest in neuroscience, meditation, and biofeedback.
Cons
- ✖Risk of oversimplification, leading to misconceptions.
- ✖Limited immediate practical application without further specialized training.
- ✖Potential for misinterpretation or supporting unverified claims.
- ✖True neurological complexity extends far beyond beginner scope.
📈 Optimizing Your Brainwave Profile
The goal of brainwave optimization isn’t to eliminate certain waves but to cultivate the ability to produce the right brainwave patterns for the right situation. A healthy brain exhibits flexibility, easily transitioning between states as needed. For example:
- For Focus & Productivity: Shift towards higher beta and gamma.
- For Relaxation & Creativity: Increase alpha and theta.
- For Deep Rest & Healing: Promote delta waves.
This dynamic interplay allows us to navigate the complexities of life, moving from periods of intense focus to moments of deep rest and creative inspiration.
🚀 How to Influence Your Brainwaves for Optimal Performance
The exciting news is that you’re not merely a passive recipient of your brainwave patterns; you can actively influence them. This is where the principles of biohacking your mind truly come into play.
🧘 Meditation and Mindfulness: Directing Your Brain’s Orchestra
Meditation is one of the most powerful and scientifically validated methods for altering brainwave states. Regular practice has been shown to:
- ✅ Increase Alpha Waves: Promoting relaxation and a calm alert state, reducing stress. Many forms of meditation are designed to cultivate this.
- ✅ Increase Theta Waves: Facilitating deeper states of introspection, creativity, and access to subconscious insights, often seen in experienced meditators.
- ✅ Boost Gamma Waves: Advanced meditative practices, particularly those focused on compassion and unified consciousness, have been linked to significant increases in gamma activity.
- ✅ Enhance Brain Plasticity: The consistent practice of meditation can lead to structural and functional changes in the brain, fostering greater adaptability and resilience. To delve deeper into these profound changes, explore articles on the impact of meditation on neuroplasticity.
Simple mindfulness exercises, such as focusing on your breath, can begin to shift your brain from a chaotic high-beta state to a more balanced alpha rhythm. For an comprehensive approach to cultivating these states, consider exploring resources on meditation and mental state control.
🧠 Neurofeedback: Training Your Brain
Neurofeedback is a non-invasive technique that directly trains the brain to modify its own activity. During a neurofeedback session, sensors are placed on the scalp to monitor brainwave activity in real-time. This activity is then “fed back” to the individual, often in the form of a game or video. For example, if the goal is to increase alpha waves, the game might only progress when alpha activity increases. This immediate feedback loop allows the brain to learn to self-regulate and produce more of the desired brainwave frequencies. Neurofeedback has shown promise in addressing various conditions, from ADHD to anxiety, by teaching individuals to optimize their own brain activity.
🎧 Sound and Light Therapy (Binaural Beats)
As mentioned earlier, sound and light therapy, particularly through binaural beats and isochronic tones, offer a passive way to encourage your brain to shift into desired brainwave states. By listening to specific frequencies, you can gently guide your brain towards states of relaxation (alpha, theta), focus (beta), or even deep sleep (delta). Many apps and audio tracks are available that utilize these principles to support various cognitive goals.
🍎 Lifestyle Factors: Supporting Your Brain’s Health
Beyond specific techniques, holistic lifestyle choices fundamentally support healthy brainwave activity:
- ✅ Quality Sleep: Non-negotiable for delta wave production and overall brain health.
- ✅ Nutrient-Rich Diet: Provides the building blocks for neurotransmitters and supports optimal brain function.
- ✅ Regular Exercise: Boosts blood flow to the brain, reduces stress, and enhances cognitive function.
- ✅ Stress Management: Chronic stress can lead to excessive beta activity; techniques like journaling, spending time in nature, and social connection are vital.
By integrating these practices, you create an environment where your brain can naturally produce optimal brainwave patterns.
The Future of Brainwave Understanding and Biohacking
Our understanding of brainwaves is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in neuroscience and technology. The ability to monitor and influence these electrical rhythms holds immense promise for the future of human performance, mental health, and well-being.
💻 Advancements in Brainwave Technology
Wearable EEG devices are becoming more accessible, allowing individuals to monitor their own brainwave activity in real-time outside of a clinical setting. These devices can provide insights into meditation depth, stress levels, and focus, empowering individuals to take a more active role in their brain health. As this technology becomes more sophisticated and integrated with AI, personalized brain training will become even more precise and effective.
🎯 Personalized Brainwave Optimization
Imagine a future where your brainwave profile is precisely understood, and personalized interventions (whether through neurofeedback, soundscapes, or even customized light therapies) are tailored to help you achieve specific cognitive and emotional states on demand. This level of personalized biohacking could revolutionize learning, productivity, stress management, and even therapy for neurological conditions.
Recommended Video
Conclusion: Harnessing Your Inner Rhythms
Brainwaves are the silent orchestrators of your mental life, dictating your states of consciousness, your ability to focus, relax, and create. By gaining a foundational understanding of alpha, theta, delta, and gamma waves, you begin to unlock the incredible potential within your own mind.
This guide serves as a starting point. The true journey lies in experimenting with practices like meditation, mindfulness, and lifestyle adjustments to consciously influence your brainwave patterns. As you learn to navigate these inner rhythms, you gain a powerful tool for enhancing your cognitive abilities, managing stress, fostering creativity, and ultimately, living a more balanced and fulfilling life. Your brain is a dynamic instrument—learn to play it well.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of brainwaves?
The primary types are Delta, Theta, Alpha, Beta, and Gamma waves, each representing different frequencies of electrical activity in the brain.
How do brainwaves affect my daily life?
Brainwaves influence everything from your ability to focus and learn (Gamma, Beta), to your capacity for relaxation (Alpha) and deep restorative sleep (Delta, Theta).
Can I influence my own brainwaves?
Yes, practices such as meditation, mindfulness, specific breathing exercises, and sound therapy (like binaural beats) can help shift and optimize your brainwave states.
Are certain brainwave states ‘better’ than others?
No, each brainwave state serves a vital purpose. The goal is balance and the ability to shift between states as needed for different tasks and situations.
